What Causes Leaky Gut?
Do you usually consume ultra-processed foods and abuse medications? Be careful because you can end up triggering a leaky gut. This can manifest symptoms on the skin and stomach, cause mental disorders and autoimmune diseases.
Keep reading everything that we are going to tell you below to learn more about the causes of leaky gut.
What Causes Leaky Gut?
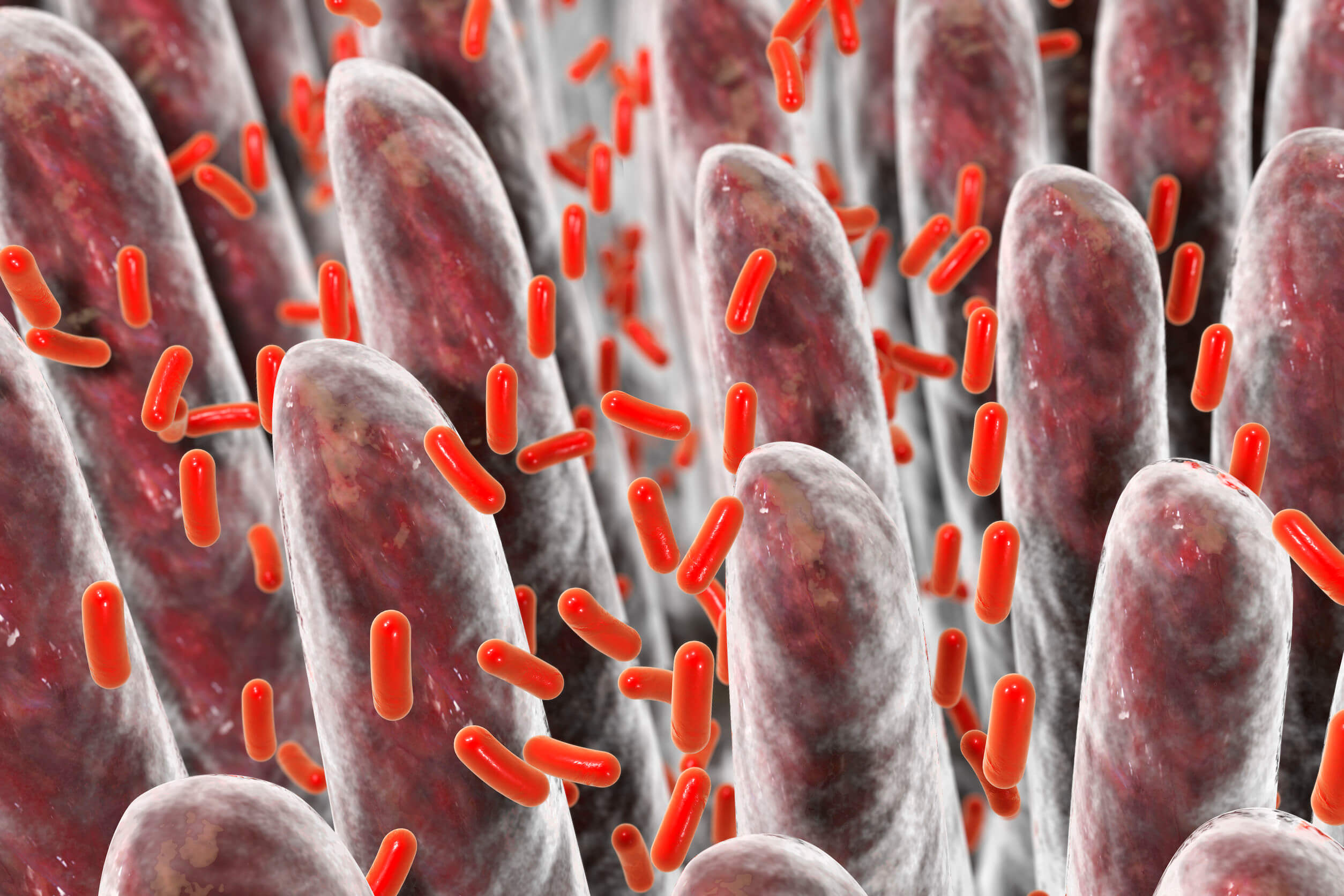
Although leaky gut is a disease that begins in the digestive system, it affects many other systems. A leaky gut occurs when enterocytes, or the proteins that attach them, are damaged.
When this happens, it increases the likelihood that some of the contents of the intestinal lumen – inside the intestine – may leak into the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
What escapes is not large chunks of food, but a combination of many different pathogens:
- Incompletely digested proteins.
- Bacteria or bacterial fragments.
- Variety of toxic substances or waste products that are normally excreted.
You should know that these substances should not exceed the intestinal barrier, since the body reacts by activating the immune system as protection against new “invaders”. The answer is so important that, if it is maintained over time, the body can end up making mistakes and even attack its own cells.
Multiple studies show how these autoimmune attacks play a role in the development of diseases such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or type 1 diabetes. This excessive immune activation leads to inflammation throughout the body.
This inflammation can affect not only the intestine itself, but also other organs and tissues such as the skeletal system, pancreas, kidney, liver, and brain.
You don’t always have intestinal symptoms with a leaky gut. But it can be expressed with:
- Migraine.
- Dysmenorrhea
- Skin problems such as eczema or psoriasis.
- Psychological disorders (depression, for example).
- Autoimmune diseases that affect the thyroid gland or joints.
Leaky Gut Cause Factors
The factors that can induce a leaky gut are the following:
- Food based on industrial products.
- Eating wheat, which can trigger certain autoimmune diseases.
- Factors that affect the regeneration of the epithelium: stress or hormonal imbalances.
- Medications that destroy the intestinal flora or affect the integrity of the epithelium : antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antacids.
How to regain intestinal permeability?

1. Avoid everything that causes intestinal inflammation
This means avoiding the following:
- Diets rich in ultra-processed, refined carbohydrates, sugar and pastries.
- Medications such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatories.
- The diets low in fiber fermentable.
- Dietary toxins such as wheat seed oils.
- Chronic stress
2. Take care of the intestinal microbiota
The human intestine contains the same number of bacteria as cells throughout the body. With more than 400 different species of bacteria, we have only recently begun to understand the role of the gut microbiota in health.
Among other things, the microbiota promotes normal gastrointestinal function, provides protection against infection, regulates metabolism, and matures the immune system.
To take care of the microbiota you must:
- Remove toxins from food from your diet.
- Maximize your digestive capacity by eating hungry and leaving space between meals for your gastric juices to act normally.
- Eat fermentable fibers: resistant starch, pectins, fructans.
- Eat fermented foods: yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, or take a quality probiotic.
- Treat the presence of intestinal pathogens: for example parasites.
3. Regulating the acidity of your stomach helps control leaky gut
Stomach acid is a basic requirement for healthy digestion. The breakdown and absorption of nutrients occurs at an optimal rate only within a narrow range of acidity in the stomach. If there is not enough stomach acid, the normal chemical reactions required to absorb nutrients deteriorate.
Low stomach acid also impairs the digestion of carbohydrates. If the pH of the stomach is too high, pancreatic enzymes will not be secreted and carbohydrates will not break down properly.
These undigested carbohydrates cause an overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine, known as bacterial overgrowth. It can also cause increased gas production and digestive discomfort.
What to watch out for about gut health?
Leaky gut has different causes, but many are linked to an unhealthy lifestyle. If we can improve our diet, avoid toxins and control stress, we will have made great strides in our intestinal health care.
If you have doubts about what you are eating, or want to start a healthy diet, remember that it is better to consult a professional nutritionist. They will know how to advise you on what is best for the intestines and your diet in general.