Tuna Vs. Salmon: Which Is The Best?

According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), fish is a source of nutrients and a traditional food in many peoples of the world. However, not all have the same characteristics. For example, if we put tuna against salmon, the latter has more fat and is a high-cost gastronomic delicacy.
While tuna, despite not being the gourmet ingredient , is of high protein value and one of the most lucrative and consumed fish worldwide.
The size, color and habitat are also different. Tuna grow in ecosystems in the ocean and adjacent seas, while some species of salmon are born in fresh water, migrate to the ocean, and return to rivers to breed. Others can be developed in hatcheries.
There are also differences in their nutritional value and in the presence of some contaminants in their meats. Do you want to know the nutritional differences and what these contaminants could be? Below we show you them so that you can select the one that suits you best.
Nutritional comparison between tuna and salmon
According to the CECOPESCA Nutritional Guide, there are important differences between the nutritional value of tuna and salmon that we will denote below.
1. Protein content and quality
From a biological point of view, the amount of essential amino acids in fish protein is higher than in meat. That is, when we eat fish we provide amino acids that the body cannot produce in proportions adjusted to what is recommended by the FAO.
The protein content of tuna is slightly higher than salmon: 22% vs. 19.8%. It also provides more essential amino acids, such as lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, and tryptophan. This ensures greater synthesis of muscle tissue, hair, nails, and better skin integrity.

2. Fat content and quality
Salmon is classified as an oily fish for its high content of unsaturated fat. It has 5 times more than tuna and is more concentrated in polyunsaturated fatty acids.
According to Valenzuela, a nutritionist, omega 3s such as eicosapentaenoic (EPA) and docosahexaenoic (DHA) are related to the well-being of the heart. Salmon stands out for a higher content of this type of fat when compared to tuna.
EPA and DHA in salmon add up to a proportion of 1.4% and in tuna they barely reach 0.3%. On the other hand, the higher fat content of salmon leads to a caloric increase in its meat. A serving of 100 grams of salmon provides 142 calories, while 100 grams of tuna represents only 100.
3. Vitamins
As for vitamins of the B complex, the niacin content is 2 times higher in tuna, with 15.4 milligrams%. For its part, salmon contains 21 micrograms% of folic acid against 9 micrograms% in tuna. Pantothenic acid or vitamin B5 is 1.3 milligrams% in salmon and 0.4 milligrams% in tuna.
Of the fat-soluble vitamins, tuna provides only slightly more vitamin A, with 15.6 micrograms%. But salmon is a vehicle for vitamin D with 10 micrograms% and vitamin E with 2 milligrams%.
4. Minerals
Tuna contains twice as much calcium as salmon, with 29 milligrams%. It also has more iron, with 1.3 milligrams% and 34 milligrams% of magnesium.
In contrast, iodine is almost double in salmon, with 50 micrograms% when compared to tuna. Salmon also contains more potassium and selenium is 36 milligrams% in both species.
Benefits of tuna versus salmon
Here we present you which are the greatest benefits of tuna compared to salmon in the comparison.
Protector of the heart
Although tuna is low in fat, its fatty acids are omega 3 and monounsaturated. There are several studies that show the prevention of cardiovascular diseases when consuming this type of fat.
Omega 3 and oleic fatty acid prevent clogging of the arteries and allow good circulation. In other words, eating tuna is keeping your heart muscle healthy.
Ideal for fitness diets
On the other hand, the high protein content and its biological quality facilitates the synthesis of muscle tissue, making it one of the preferred foods for fitness diets . Lean or low-fat protein allows you to select tuna for low-calorie meal plans.
Strengthen the immune system
The high content of selenium in tuna is beneficial to protect the body against oxidizing agents. Vinchira, a veterinarian, discusses the potential effects of selenium in sources like fish to improve immune function, thyroid activity, and fertility.
Change the mood
Eating tuna is to incorporate a series of nutrients related to well-being and the reduction of depression. There are numerous studies and meta-analyzes that link omega 3 fatty acids to a reduction in depression and an improvement in mood, especially in certain critical stages of life.
Provides minerals and vitamins
Tuna is an important source of iron to increase hemoglobin, since it is easily absorbed. Likewise, the levels of potassium, iodine, magnesium and phosphorus allow the regulation of many functions in the body.
On the other hand, tuna also provides an excellent amount of niacin or vitamin B3. According to the Mayo Clinic, this vitamin is capable of keeping the nervous system, digestive system and skin healthy. They also have scientific evidence that associates it with an increase in HDL cholesterol or good cholesterol .
Benefits of salmon versus tuna
Now, on the other hand, we will tell you the benefits of salmon if we compare it with tuna.
Protector of the heart, nervous system and vision
The Chilean Nutrition Magazine points out that salmon contains very high levels of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids of the omega 3 series, also known as AGPCL. The best known, as in tuna, are eicosapentaenoic (EPA) and docosahexaenoic (DHA). EPA is associated with cardiovascular health and DHA with the formation and function of the nervous and visual systems.
Salmon is also one of the few foods that provides more DHA than EPA. 2 to 3 servings of the fish are needed to ensure the recommendations for these fatty acids.
Important source of vitamin D and E
Vitamin D facilitates the absorption and fixation of calcium to the bones, while vitamin E is a natural antioxidant that, in addition to preventing the oxidation of salmon fat, prevents oxidation-reduction reactions of different cell tissues.
A serving of salmon of approximately 70 grams covers 70% and 23% of the recommended intake of vitamin D and E, respectively, for men and women aged 20 to 39 years.
Salmon provides DHA for the brain
Studies have observed that DHA deficiency during the perinatal period alters a child’s ability to learn, concentration, and IQ until adulthood.
In the British Journal of Nutrition they recommend an adequate supply of DHA with the diet to prevent its loss in neurons. This can reduce the incidence of Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s and other neurological degenerations. Consuming 2 servings of salmon provides enough DHA.
Salmon as a source of folic acid
The folic acid content of salmon is 10 times higher than that of tuna. The Bengoa Foundation describes the benefits of this vitamin of the B complex, capable of helping to control hypertension, prevent anemia and participate in the formation of the nervous system.
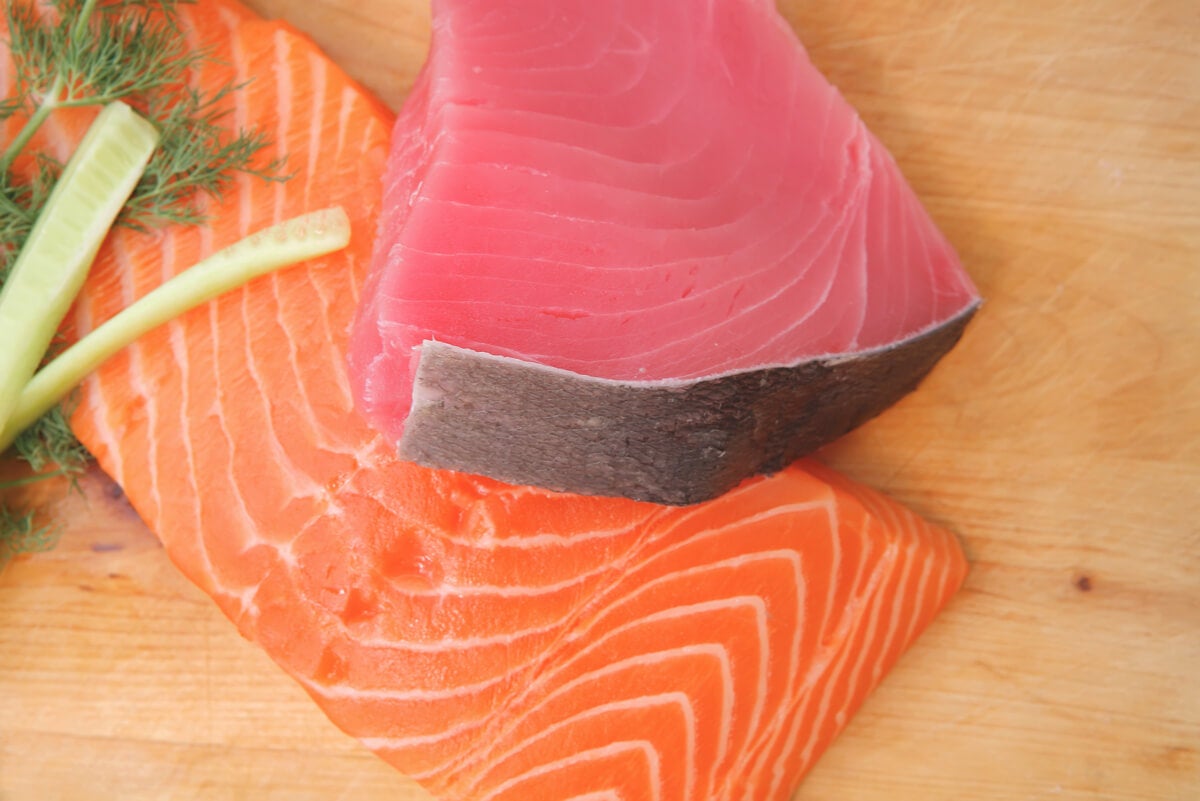

The color of salmon is also healthy
The orange-pink color of salmon is due to the presence of a carotenoid-like pigment produced by the microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis , called astaxanthin .
At present, it is recognized by a group of researchers as a powerful antioxidant that protects the skin and eyes against external aggressions, fights inflammatory pain and improves sports performance.
Beware of mercury and dioxin
Some marine species concentrate mercury in their body. These concentrations can affect health, producing poisoning.
According to Balshaw, the more fat the tuna has, the less mercury concentration it will have in its meat. Bluefin tuna contains more mercury than salmon, which, due to its minimal quantities, does not present consumption limits.
However, farmed salmon can accumulate dioxin, a pollutant that affects liver function and leads to skin lesions. The WHO Cancer Research Center has classified it as a human carcinogen. However, the dioxin values in farmed salmon are very low in relation to the high benefit of its fat.
Tuna or salmon?
To choose the fish of your choice you must consider the health or nutrition goal you are pursuing. For example, if you need to protect your heart, the best choice will be to eat salmon, but if you want to stay in shape, tuna is the best ally.
However, variety is a key that allows you to incorporate different nutrients into a long-term plan. That is why we encourage you to combine and include both types of fish.