Vigorexia And The Consequences Of An Obsession With The Perfect Body

We speak of vigorexia or inverse anorexia when a person has an extreme obsession with the image of their body. This comes from a distortion in the perception of the figure, which is why it is also called “muscle dysmorphia.”
The disorder is more common among men and is expressed, in general, with excessive attendance at gymnasiums for weight training. We are going to tell you in this article what are the symptoms and consequences of this serious pathology.
What is vigorexia?
Vigorexia or obsession with the body figure is a dysmorphic disorder. This means that it is a disease in the field of mental health in which people do not allow themselves to have defects in appearance.
From this, the image of the body becomes the central theme on which existence revolves. Patients with the problem live looking in the mirror, reviewing the lines of their body, consuming information about gyms and diets, as well as ordering their routine in pursuit of a supposed external beauty.
It is related to obsessive compulsive disorders, since distortion in perception is the recurring theme, while compulsion is expressed in the repetition of acts that would achieve the objective of improving the figure. One of them could be the habit of looking at yourself in a mirror.
Vigorexia affects many aspects of people’s lives and not just the physical. These are individuals who tend to isolate themselves from certain relationships due to the time they spend on so-called beautification activities. In the same way, they receive comments about their body weight in a bad way, for example.

Who is most at risk?
Statistics indicate that vigorexia is most commonly diagnosed in males who are under 35 years of age. A high prevalence has also been registered among those whose favorite activity is bodybuilding, reaching up to 10% of these athletes.
There is also a link between personalities with addiction traits and suffering from this disorder. Up to 15% of patients are also habitual consumers of alcohol and tobacco. A slightly lower percentage regularly use other illegal drugs, such as marijuana or cocaine.
One particular group at high risk is those who are overweight who enroll in intensive weight loss programs.
Symptoms and consequences of vigorexia
A primary sign of vigorexia is excessive training. People with the disorder adapt their daily routine around attending sports and gymnastic activities that affect their body shape.
Although they receive recommendations from specialists and acquaintances, they turn a deaf ear. They do not accept criticism and comments about their obsession, and they consider that others are wrong or have a distorted idea of what they do.
In men, the constant search is to increase muscle mass and define them. For this reason, weight lifting is the activity that is usually established as a fixed one, several times a week.
Diet and eating is another pillar of symptoms. Very restrictive plans are made, with little calorie intake and lacking in basic nutrients. Low kilocalorie density leads to long-term problems ranging from anemia to hypovitaminosis.
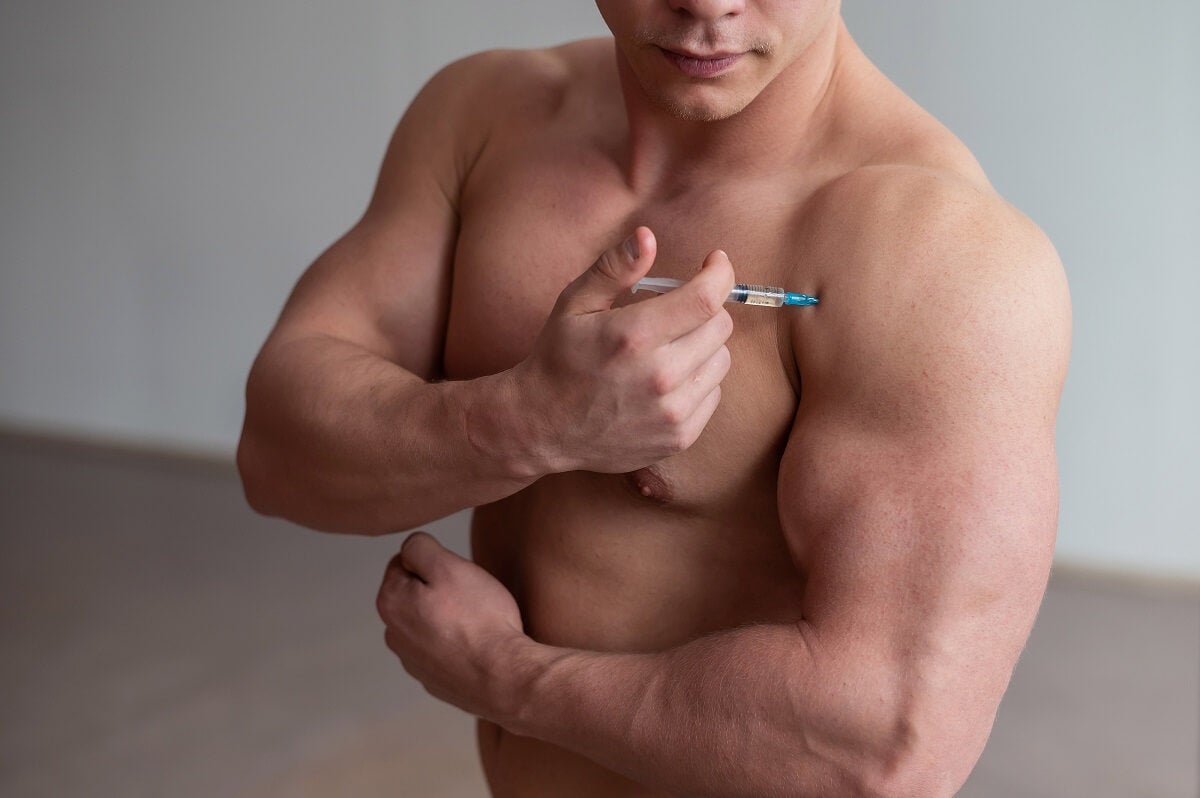
The use of anabolic and steroid drugs that accelerate muscle mass gain is another serious problem with vigorexia. In the desperate search to improve their figure, people with the disorder put their internal hormonal systems at risk by consuming them. The consequences of these drugs are as follows:
- Testicular atrophy in males: along with a decrease in libido or sexual desire.
- Masculinization in women: appearance of secondary sexual characteristics typical of men.
- Stopping bone growth in young individuals: up to the age of 25 the bone continues its extension process, which can be slowed down or ended by the action of steroids.
- Increase in bad cholesterol or LDL: with the consequent cardiovascular risk.
- Hepatic peliosis: formation of blood cysts in the liver.
Available treatments
The therapeutic approach to vigorexia is based on behavior modification therapy. Body perception is worked to bring it back to the reality of what happens and what is perceived.
The close and social support group is essential in recovery. A network of family support and friends committed to accompanying them can support the change of routines so that other problems do not appear, such as depression or anxiety.
The use of hypnosis or neurolinguistic therapy has been studied with research. In theory, they would speed up the treatment process if they are performed by professionals trained in these techniques.
Take care of the body, but do not obsess
Sometimes milder forms of vigorexia show up in ways of exercising and eating. Perhaps not as an extreme obsession, but it does lead to modifying routines in pursuit of an ideal body that cannot be defined as such either.
It is important to take care of yourself, but you have to identify the limits so as not to fall into serious health consequences. Evaluate your exercise and eating practices and consider how healthy they are or not. It is a good introspection task to also take care of yourself on a psychological level.